Cottonwood borer
Plectrodera scalator (Fabricius) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae)
Orientation to pest
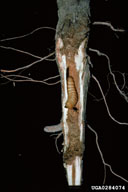
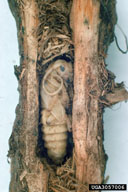
Cottonwood borer, Plectrodera scalator (Fabricius), is a native insect that attacks cottonwoods and poplars (Populus), willows (Salix), and species of Platanus, Albizia, and Helianthus. Adults first emerge in late spring and feed on the shoots of young trees. Mating and egg-laying occur throughout the summer. Females dig away soil from the base of the tree, where they cut a niche in the bark, and deposit one or several eggs. Larvae feed in the bases and roots of live trees of all sizes. At first larvae mine the inner bark, but by fall larvae bore into the wood. Two or more growing seasons are required for larval development. In their last year, the large larvae create tunnels at the base of the tree, where they pupate the falling spring. New adults emerge by chewing through the pupal chamber and digging their way out of the soil. Young trees may be hollowed out, partially severed, or girdled near the root collar, causing breakage. Greatest damage occurs to trees in plantations and nurseries, and young stands on sandy soils.
Hosts commonly attacked
This borer attacks cottonwoods and poplars (Populus), willows (Salix), and species of Platanus, Albizia, and Helianthus
Distribution
The cottonwood borer is found New York to Montana and south to Texas. Damage is greatest in the southern United States.
Images of cottonwood borer
| Figure 1. Adult of cottonwood borer, Plectrodera scalator | Figure 2. Adult female of cottonwood borer deposting an egg below the soil line into a young cottonwood shoot. | ||
| Figure 3. Larvae of cottonwood borer in root of eastern cottonwood (Populus deltoides ssp. deltoides Bartram ex Marsh.) (left) or stem of young tree (right). | Figure 4. Pupa of cottonwood borer in cottonwood shoot | Figure 5. Two views of damage from cottonwood borer at base of cottonwood rootstocks | |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
Little is known of the natural enemies of this species, except that cottonwood borer is sometimes parasitized by the sarcophagid fly Sarcophaga vericauda Hungerford, or parasitic wasps in the genera Ibalia, Rhyssa, or Megarhyssa. It is also susceptible to applications of the fungal biopesticide Beauveria bassiana.
Web links for information on cottonwood borer
- Digital Diagnostics Fact Sheet | Oklahoma State University
- Fact Sheet on ForestPests.org | USDA Forest Service, Southern Forest Experiment Station
Articles
- Solomon, J. D. 1980. Cottonwood borer (Plectrodera scalator) - a guide to its biologv, damage, and control. Research Paper SO157. New Orleans, LA, U.S. Department of Agriculture. Forest Service, Southern Forest Experiment Station. 10 pp.
- Forschler, B. T. and G. L. Nordin. 1989. Impact of Beauveria bassiana on the cottonwood borer Plectrodera scalator (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), in a commercial cottonwood nursery. Journal of Entomological Science 24(2): 186-190.