Spearmarked black moth
Rheumaptera hastata (L.) (Lepidoptera: Geometridae)
Orientation to pest
Spearmarked black moth, Rheumaptera hastata (L.), is a native North American looper found from North Dakota to British Columbia and Alaska. It feeds mainly on birch (Betula). Adults fly in spring. In Alaska, eggs are laid singly or in clusters on tops of leaves, from mid-June to early July. Young larvae feed gregariously between two leaves webbed together to make a sandwich-type shelter. Larvae feed on both new and old-growth foliage and usually feed just on the upper side, skeletonizing leaves. Larvae mature in July and August, drop to the ground on silken threads and pupate in the leaf litter, where they overwinter. There is one generation per year. This moth is a serious defoliator of paper birch (Betula papyrifera Marsh.) in interior Alaska. Epidemic populations have occurred at 15- to 17-year intervals, persisted for 2 years, and then collapsed from natural causes.
Hosts commonly attacked
This species feeds mainly on mainly on birch (Betula spp.). In Alaska, paper birch (Betula papyrifera Marsh.) is the preferred host, but larvae also feed on species of alder (Alnus), willow (Salix), and rose (Rosa). In Canada, the insect also feeds on sweetgale (Myrica).
Distribution
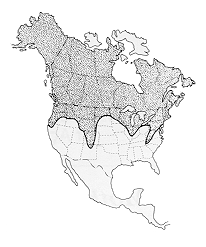
This geometrid is found throughout Canada and Alaska, and the northern United States, with southerly range extensions along mountain chains (Cascades, Rockies, Appalachians).
 USDA Forest Service • Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 156 USDA Forest Service • Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 156 |
| Figure 1. North American distribution of spearmarked black moth, Rheumaptera hastata |
Images of spearmarked black moth
| Figure 1. Adult of spearmarked black moth, Rheumaptera hastata | Figure 2. Life stages (adult, eggs, larva, pupae) of spearmarked black moth | Figure 3. Larva of spearmarked black moth |
| Figure 4. Tent made by larva of spearmarked black moth, where it feeds | Figure 5. Birch defoliated by spearmarked black moth |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
Parasitoids that have been reared from the overwintering pupae of this moth include Aoplus ruficeps vagans Provancher (Ichneumonidae), Coccygomimus aquilonius (Ichneumonidae), and Cratichneumon sp. (Ichneumonidae). The parasitoid Meteorus niveitarsis Cresson (Braconidae) has been reared from larvae.
Web links for information on spearmarked black moth
Articles
- McGuffin, W. C. 1973. The Rheumaptera of North America (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). The Canadian Entomologist 105:383-389.
- Werner, R. A. and B. H. Baker. 1977. Spear-marked black moth. Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 156. (Portland, OR). U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Forest and Range Experiment Station.
Viewable online at http://www.ncrs.fs.fed.us/pubs/viewpub.asp?key=965 - Werner, R. A.1977. Biology and behavior of the spear-marked black moth, Rheumaptera hastata, in interior Alaska. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 70: 328-336.








