Western pine beetle
Dendroctonus brevicomis LeConte, (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae])
Orientation to pest
Western pine beetle, Dendroctonus brevicomis LeConte, is a native bark beetle of the western United States that attacks and kills ponderosa (Pinus ponderosa Douglas ex P & C. Lawson) and Coulter (Pinus coulteri D. Don) pines greater than 15 cm in diameter, regardless of age or vigor, including apparently healthy trees. Outbreaks are most common in dense, even-age stands, but also occur in areas of mixed conifer species. Mortality is often subtle yet significant when large old trees are killed individually by the beetle. Large outbreaks are common and over one million trees (more than 1 billion board feet of timber) may be killed each year during outbreaks. Outbreaks have been known to occur following wildfires in ponderosa pine stands. Beetle attacks are first visible due to pitch tubes that form at the sites where female beetles bore into the tree to create oviposition galleries. However, pitch tubes of this species are less conspicuous than for other bark beetles and frequently are not seen at all. Attacking adult beetles carry spores of a blue-staining fungus, Ceratocystis minor (Hedg.), which contributes to tree death by blocking the water-conducting vessels in the wood. The egg galleries are about the width of an adult beetle and are usually tightly packed with boring dust. There are two to four generations per year, depending on latitude and altitude. Eggs are laid singly along the oviposition gallery and larvae then make short lateral galleries as they feed. As is true for many bark beetles, aggregation pheromones produced by the beetle coordinate a mass attack on selected trees. Thinning of trees to reduce density can be used to reduce stand susceptibility to mortality from western pine beetle.
Hosts commonly attacked
This beetle attacks ponderosa (Pinus ponderosa Douglas ex P & C. Lawson) and Coulter (Pinus coulteri D. Don) pines.
Distribution
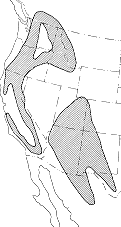
Western pine beetle is most damaging in California, but its range extends northward into Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and southern British Columbia, as well as eastward into Montana, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, New Mexico, and western Texas. It also occurs in northwestern Mexico.
 USDA Forest Service • Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 1 USDA Forest Service • Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 1 |
| Figure 1. Distribution (in western North America) of the western pine beetle, Dendroctonus brevicomis |
Images of western pine beetle
| Figure 2. Adult of western pine beetle Dendroctonus brevicomis (left) and close up of head (right); note lack of rows of tubercules on either side of the frontal groove, as are present in the southern pine beetle (Dendroctonus frontalis (Zimmermann). | Figure 3. Pitch tubes of western pine beetle | |
| Figure 4. Larvae of western pine beetle | Figure 5. Galleries of western pine beetle in ponderosa pine | |
| Figure 6. Shot holes formed in ponderosa pine by emergence of western pine beetles | Figure 7. Two views of stands of ponderosa pines killed by western pine beetle | Figure 8. The predacious clerid beetle Enoclerus lecontei, a predator of western pine beetle | |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
Important predators of brood of western pine beetle are the clerid beetles Enoclerus lecontei (Wolcott) and Enoclerus sphegeus Fabricius, as well as the blue-green ostomid Temnochila chlorodia Mannerheim and the fly Medetera aldrichii Wheeler. Common parasites are Roptrocerus xylophagorum Ratzeburg, Dinotiscus burkei Crawford, and Coeloides sp. nr. brunneri Vierick.
Web links for information on western pine beetle
- Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 1 | USDA Forest Service
- Fact Sheet | Nevada Division of Forestry, State of Nevada
Articles
- Miller, J. M. and F. P. Keen. 1960. Biology and control of the western pine beetle.. U.S. Department of Agriculture Misc. Publ. 800, Washington, DC. 381 p.
- Stark, R. W and D. L. Dahlsten (eds.). 1970. Studies on the population dynamics of the western pine beetle, Dendroctonus brevicomis LeConte (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). University of California, Division of Agricultural Science, Berkeley, California, USA. 174 pp.
- Wallin, K. F., T. E. Kolb, K. R. Skov, and M. Wagner, M. 2008. Forest management treatments, tree resistance, and bark beetle resource utilization in ponderosa pine forests of northern Arizona. Forest Ecology and Management 255 (8/9): 3263-3269.













