Eastern pine weevil
Pissodes nemorensis Germar (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
Orientation to pest
Eastern pine weevil, Pissodes nemorensis Germar, is now the name that is applied to what was formerly known as northern pine weevil (Pissodes approximatus Hopkins), which is no longer considered a valid species. Eastern pine weevil is native to North America, where it feeds on cedars (Cedrus) and pines (Pinus). In the southern United States, adults are active in fall, winter and spring, and are inactive in summer. Eggs are laid in the spring in stems or branches. The northern form appears to commonly breed also in stumps of cut trees and becomes a pest in plantations as numbers build up. Larvae feed in the cambium and pupate in the wood in cells make of wood chips. Adults feed on branches and terminals, which may be killed, leading to bushiness or crooked stems. Small trees may be killed by larval feeding.
Hosts commonly attacked
In the northern part of its range, eastern pine weevil breeds in pines, especially red (Pinus resinosa Sol. ex Aiton) and Scots (Pinus sylvestris L.) pines. In the southern United States, both cedars and pines are attacked. Cedars used as hosts include both native species and exotic cedars such as deodar cedar (Cedrus deodara [Roxb.] G. Don), Atlas cedar (Cedrus atlantica [Endl.] Manetti ex Carrière), and cedar of Lebanon (Cedrus libani A. Rich.). In the southern USA, various North American pines are used as hosts, especially loblolly (Pinus taeda L.), shortleaf (Pinus echinata Mill.), and longleaf (Pinus palustris Mill.)
Distribution
The southern form of this weevil is found in the southeastern United States, north to Pennsylvania. The northern form (the old P. approximatus) is found from the Atlantic coast to Manitoba and Minnesota and south to North Carolina. The species is not present in the western United States. It is an invasive pest in some countries, including South Africa, where it is a pest in plantations of exotic pines.
Images of eastern pine weevil
| Figure 1. Adult of eastern pine weevil, Pissodes nemorensis | Figure 2. Eggs of eastern pine weevil | |
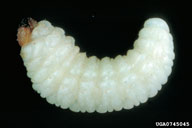
| Figure 3. Larvae of eastern pine weevil feeding in gallery (left) and mature larva (right) ready for pupation | Figure 4. Pupa of eastern pine weevil in cocoon (top), and cocoons on trunk with bark removed (bottom) | |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
The braconid parasitoid Coeloides pissodis (Ashmead) is an important natural enemy of eastern pine weevil.
Web links for information on eastern pine weevil
- BugwoodWiki Article | wiki.bugwood.org
- Quarantined Pest Data Sheet | European & Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization
- Fact Sheet | Forestry and Agricultural Biotechnology Institute
Provides detailed information on biology and management of pest in South Africa
Articles
- Gebeyehu, S. and M. J. Wingfield. 2003. Pine weevil Pissodes nemorensis: threat to South African pine plantations and options for control. South African Journal of Science 99 (11/12): 531-536.