Saratoga spittlebug
Aphrophora saratogensis (Fitch) (Hemiptera: Cercopidae)
Orientation to pest
Saratoga spittlebug, Aphrophora saratogensis (Fitch), is a native insect in North America whose adults damage certain pines, especially red pine (Pinus resinosa Sol. ex Aiton), usually when grown in plantations. Damage also occurs on jack (Pinus banksiana Lamb.) and Scots pines (Pinus sylvestris L.). Adult feeding damages pines because toxics injected into the plant kill tissues, causing dead pockets of xylem and phloem tissue. Extensive feeding kills branches, stunts and deforms shoots, and may sometimes kill trees. This species is generally considered the most serious sap-feeding pest of red pine plantations. In contrast, nymphs are not pests because they feed on different plants. Young nymphs feed on understory plants such as brambles (species of Rubus), orange hawkweed (Pilosella aurantiaca [L.] F. W. Schultz and Schultz-Bip), pearly everlasting (Anaphalis nubigena DC.), and asters (Aster), while older nymphs are found on sweetfern (Comptonia peregrine [L.] J. M. Coulter) and young willows (Salix). Saratoga spittlebug has one generation each year. On red pine, eggs are laid under the outer scales of buds in the upper branches. Selection criteria have been developed that use information on nymphal host plant abundance to pick sites for new red pine plantations that will have low risk of damage from Saratoga spittlebug. A site-risk diagram has been developed for this purpose (see figure in USDA Forest Service leaflet at http://www.na.fs.fed.us/spfo/pubs/fidls/saratoga/saratoga.htm).
Hosts commonly attacked
Saratoga spittlebug is known as a pest of some pines, especially red pine (P. resinosa) grown in plantations.
Distribution
This insect occurs where ever its hosts grow, from Maine to Minnesota in the United States and in the southern portions of the adjacent Canadian Provinces. It is of particular importance in Michigan and Wisconsin.
Images of the Saratoga spittlebug
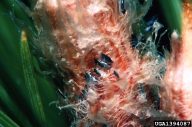
| Figure 2. Eggs of Saratoga spittlebug (dark bodies in woolly mass) | ||
| Figure 1. Adults of Saratoga spittlebug, Aphrophora saratogensis | Figure 3. Spittle masses of Saratoga spittlebugs at base of stems of sweetfern, the favorite host of older nymphs | Figure 4. Saratoga spittlebug feeding damage to red pine |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
Eggs of Saratoga spittlebug are attacked by two parasitoids, Ooctonus aphrophorae Milliron and Tumidiscapus cercopiphagus Milliron, but attack rates are low (<5%). A fly in the family Pipunculidae, Verrallia virginica Banks, may be a significant source of mortality (causing up to 50% mortality).
Web links for information on the Saratoga spittlebug
- Forest Insect & Disease Leaflet 3 | USDA Forest Service
- Fact Sheet from Maine Forest Service | State of Maine Department of Conservation
Articles
- Wilson, L. F. 1971. Risk-rating Saratoga spittlebug damage by abundance of alternate-host plants. Research Note NC-110, North Central Forest Experiment Station, Forest Service, United States Department of Agriculture, 4 pp.,
- Linnane, J. P. and E. A. Osgood. 1977. Verrallia virginica (Diptera: Pipunculidae) reared from the Saratoga spittlebug in Maine. Proceedings of the Entomological Society of Washington 79 (4): 622-623.