Lodgepole cone moth
Eucosma rescissoriana Heinrich (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae)
Orientation to pest
The lodgepole cone moth, Eucosma rescissoriana Heinrich, is found in northwestern North America south to central California. It is highly destructive to cones and seeds of western white pine (Pinus monticola Douglas). In British Columbia, adults emerge in May, and oviposition occurs in early June; in Idaho, oviposition is in June. Eggs are laid under scale tips of second-year cones. Larvae burrow in cones of host plants, consuming the seeds. Pupae overwinter, presumably, in the duff. There is one generation per year. While a pest in seed orchards in North America, it is considered to be a potential biological control agent of P. monticola in New Zealand, where this pine is invasive outside of plantations.
Hosts commonly attacked
In North America, this moth attacks western white pine (P. monticola).
Distribution
This moth occurs in North America from British Columbia and western Alberta south as far as central California and New Mexico.
Images of lodgepole cone moth
| Figure 1. Adult of lodgepole cone moth, Eucosma rescissoriana | Figure 2. Eggs of lodgepole cone moth on cone scale | Figure 3. Larvae of lodgepole cone moth hatching from eggs on cone scale |
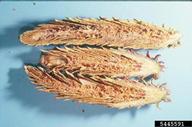
| Figure 4. Larvae of lodgepole cone moth inside cone | Figure 5. Appearance of early stage of damage to cone of western white pine by lodgepole cone moth | Figure 6. Internal feeding and damage to cone of western white pine caused by lodgepole cone moth |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
Twelve species of parasitic insects were found to be associated with E. rescissoriana in western white pine cones in northern Idaho, of which the three most abundant species were Pimplopterus n. sp. (Ichneumonidae), Chelonus petrovae McComb (Braconidae), and Apanteles starki Mason (Braconidae). Total parasitism ranged from 9.4 to 40.9% in a seed-production area over three years.
Articles
- Ollieu, M. M. and J. A. Schenk. 1966. The biology of Eucosma rescissoriana Heinrich in western white pine in Idaho (Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae). The Canadian Entomologist 98: 268-274.
- Goyer, R. A. and J. A. Schenk. 1969. Parasitism of the cone moth Eucosma rescissoriana (Lepidoptera: Olethreutidae) in northern Idaho. The Canadian Entomologist 101: 1063-1069.
- Brockerfoff, E. G. and M. Kay. 1998. Prospects and risks of biological control of wilding Pinus contorta in New Zealand. Proceedings of the 51st New Zealand Plant Protection Conference, pp. 216-223.