Rosy gypsy moth
Lymantria mathura Moore (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae)
Orientation to pest
Rosy gypsy moth, Lymantria mathura Moore, is an Asian defoliator not yet present in the United States, but one that poses a high risk of invasion and potential damage. It defoliates a variety of hardwood species and outbreaks may affect large areas. During outbreaks, the pest population density may reach 1000 caterpillars per tree. The species overwinters as eggs containing fully developed larvae, ready to hatch. Larvae emerge early in spring and disperse and attack buds, then leaves. Most feeding occurs at night. Mature larvae pupate in flimsy cocoons on the host tree. Females fly at night (1:00-3:00 AM) and lay eggs in masses of 150-600 on bark of host tree or other objects. There is one generation per year.
Hosts commonly attacked
Rosy gypsy moth attacks many species of Betula, Castanea, Juglans, Malus, Quercus, Salix, Tilia, Ulmus and other deciduous trees. Its preferred hosts in the Russian Far East include Juglans mandshurica Maxim., Quercus mongolica Fisch. ex Turcz., and Quercus dentate Thunb.
Distribution
Rosy gypsy moth is native to Asia and is found in the Russian Far East, Nepal, Japan, Korea, northern India, and parts of China (Hebei, Heilongjiang, Jilin provinces, and western China.
Images of rosy gypsy moth
| Figure 1. Adults of rosy gypsy moth, Lymantria mathura (left, male; right, female) | Figure 2. Comparison of the female of rosy gypsy moth (bottom) to that of gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar [L.]), top. |
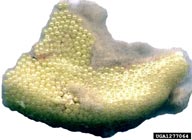
| Figure 3. Egg mass of rosy gypsy moth | Figure 4. Young larvae of rosy gypsy moth | Figure 5. Mature larvae of rosy gypsy moth | Figure 6. Pupa of rosy gypsy moth |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
In Korea, natural enemies associated with rosy gypy moth include Cotesia melanoscela (Ratzberg), the dominant larval parasitoid and Brachymeria lasus (Walker), the most important pupal parasitoid.
Web links for information on rosy gypsy moth
- Quarantined Pest Data Sheet | European & Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization
- CAPS PRA | USDA APHIS
A mini risk assessment of Rosy Gypsy Moth
Articles
- Zlotina, M. A., V. C. Mastro, D. E. Leonard, and J. S. Elkinton. 1998. Survival and development of Lymantria mathura on North American, Asian, and European tree species. Journal of Economic Entomology 91: 1162–1166.
- Anon. Lymantria mathura. 2005. EPPO Bulletin 35(3): 464-467.