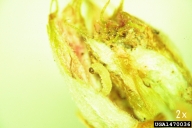
Oak leafroller
Archips semiferanus (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae)
Orientation to pest
Oak leafroller, Archips semiferanus (Walker), is native to North America, where it is widely distributed in the eastern half of the continent. Females lay eggs in masses of 40 to 50 eggs on branches or rough bark in July. Eggs overwinter and larvae emerge in spring and feed on buds and young leaves. Mid-to-late instar larvae roll leaves together with silk to form a nest in which they feed. Mature larvae pupate in the leaf rolls or crevices in June and adults emerge a few weeks later. Periodic outbreaks of this species have occurred in oak forests in North America since the 1960s. In Pennsylvania and Michigan, hundreds of thousands of acres have been defoliated in some years, with substantial tree mortality and economic loss.
Hosts commonly attacked
Larvae of oak leafroller feed on a range of oaks (Quercus), especially northern red (Quercus rubra L.), scarlet (Quercus coccinea Muenchh.), chestnut (Quercus prinus L.), and white (Quercus alba L.) oaks. In addition, this moth sometimes feeds on species of witch hazel (Hamamelis) and apple (Malus).
Distribution
Archips semiferanus is found in southeastern Canada and the eastern United States, west to Colorado and Texas.
Images of oak leafroller
| Figure 1. Adults of oak leafroller, Archips semiferanus | Figure 2. Larva of oak leafroller |
Important biological control agents related to this pest species
Natural enemies of this species have been studied in Pennsylvania where pupae were attacked by two ichneumonids, Itoplectis conquistor (Say) and Phaeogenes gilvilabris Allen, and larvae attacked by various tachinids. Larval parasitism was more common than pupal parasitism.
Web links for information on oak leafroller
Articles
- Freeman, T. N. 1958. The Archipinae of North America. The Canadian Entomologist, Supplement No. 7, 89 pp.
- Chapman, P. J. and S. E. Lienk, S. E. 1971. Tortricid fauna of apple in New York; including an account of apples' occurrence in the State, especially as a naturalized plant. New York State Agricultural Experiment Station, Special Publication, Geneva, New York, 142 pp.
- Wilson, L. F. 1972. Life history and outbreaks of an oak leafroller, Archips semiferanus (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), in Michigan. Great Lakes Entomologist 5: 71-77.
- Mumma, R. O. and A. S. Zettle. 1977. Larval and pupal parasites of the oak leafroller, Archips semiferanus. Environmental Entomology 6: 601-605.